
The POCT coordinator is responsible for resolving commonly encountered problems associated with instrument maintenance, QC, procedural issues, reporting results, training and they also provide guidance to POCT operators. However, no comparable attempt in a North American setting has been published to our knowledge and it remains unclear how this approach compares to other reassessment approaches such as auto-recertification.Īnother intervention to ensure effective compliance is to assign a senior level laboratory technologist as the POCT coordinator. The observations helped to identify common non-compliance issues, knowledge gaps and areas for improvement.
#Istat competency checklist iso#
A study by Tongtoyai, Tientadakul, & Chinswangwatanakul in Bangkok, Thailand described the development and use of two forms, one for on-site inspection and one for staff competency assessment to directly evaluate the implementation of ISO 22870:2006 standards. The methods for doing so, however, remain fledgling. It remains unclear, however, whether these are adequate measures of compliance with standards of operations.Īs an answer to the limitations of auto-recertification, some accreditation programs suggest complementing them by using direct observation of routine patient testing to assess operator competency. As such, certification does not expire for operators who regularly perform POCT as they can easily meet the minimum criteria for auto-recertification. To be auto-recertified, meter operators must successfully perform a specified number of QC runs and/or patient tests within a defined period of time. For that purpose, many institutions rely on the auto-recertification feature available in most POCT data management systems.
#Istat competency checklist how to#
Some accreditation standards also require a quality assurance program to monitor the performance and compliance of operators with policies and procedures, but they do not provide specific guidelines on how to meet this standard. Following this initial certification, user competency must be re-assessed periodically to ensure satisfactory levels of competence with the most common period for recertification being annually. To address these issues, accreditation programs require operators to complete training before being authorized to perform POCT this commonly involves hands-on training and learning the relevant principles of the test, the importance of quality assurance, how to properly interpret results, and the limitations of the test. Consequently, the accuracy and precision of a result is sensitive to the variability in skill level of a POCT operator, ,, ]. However, one challenge of POCT is that results generated by meter operators are typically less accurate than the central laboratory method because of errors in the pre-analytical and analytical phases of testing, which corresponds to POCT maintenance, Quality Control (QC) testing and the patient testing process. POCT is also beneficial in that testing only requires a small volume of blood from the patient only 0.3–1 μL of blood compared to a volume of 1–3 mL for the central laboratory glucose test, which is especially important when diabetic patients require multiple blood draws across their hospitalization. Īs an alternative, glucose point-of-care testing (POCT) allows for testing to be performed at or near the patient’s bedside, providing an immediate result. Plasma glucose testing traditionally performed in the central laboratory has a turnaround time of 30–60 min from the time of a clinician’s order to the review of a result. Fast and accurate results are especially critical for diabetic patients requiring blood glucose control within narrow therapeutic ranges. Failure to provide immediate results impedes physician decision making, negatively impacts patient quality of care, and results in greater healthcare costs associated with the management of hypo- or hyperglycemic episodes. Early identification, effective treatment and glucose monitoring of diabetic patients can help reduce these outcomes.

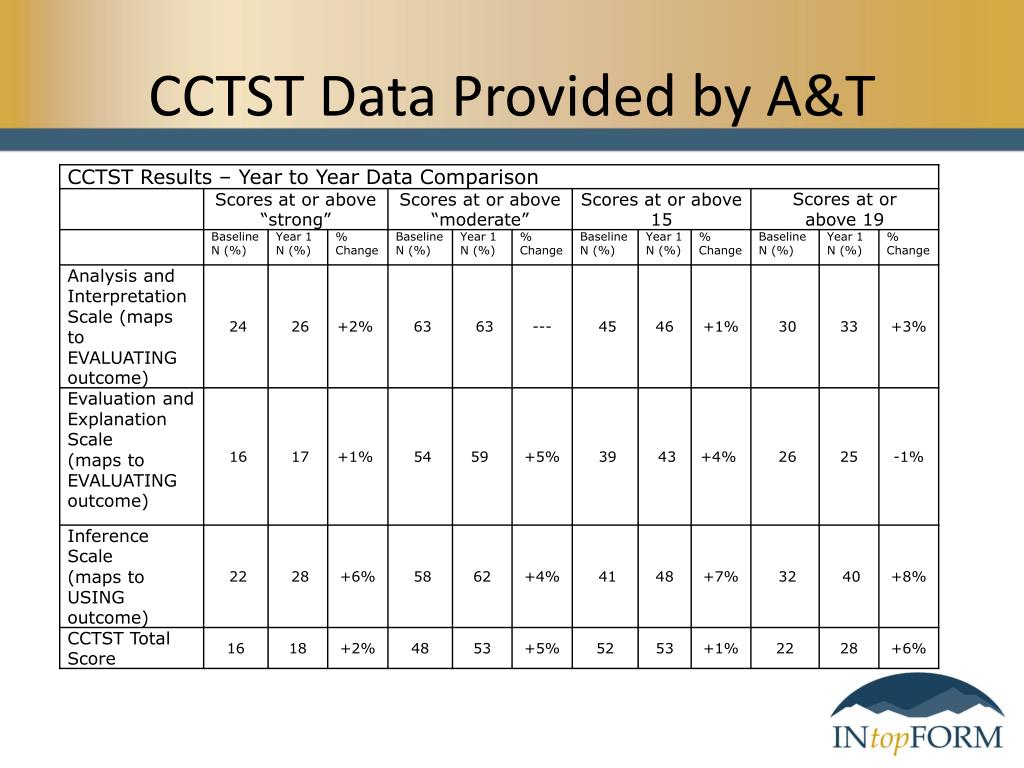

Hospitalized diabetic patients who experience episodes of hypoglycemia and/or hyperglycemia have poorer health outcomes, increased mortality and increased lengths of stay.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
